Research finds trigger to stress-related obesity
WASHINGTON – Scientists reported Sunday that they have uncovered a biological switch by which stress can promote obesity, a discovery that could help explain the world’s growing weight problem and lead to new ways to melt flab and manipulate fat for cosmetic purposes.
In a series of experiments on mice, researchers showed that the neurochemical pathway they identified promotes fat growth in chronically stressed animals that eat the equivalent of a junk-food diet.
The international team also showed that blocking those signals can prevent fat accumulation and shrink fat deposits, while stimulating the pathway can strategically create new ones, possibly offering new ways to remove fat as well as to mold youthful faces, firmer buttocks and bigger breasts.
“It’s very exciting,” said Zofia Zukowska of Georgetown University, who led the research published online by the journal Nature Medicine. “This could be revolutionary.”
The researchers have applied for a patent and begun negotiating with drug companies to license the technology. They predicted studies in people could begin within two years.
Previous studies have indicated that while acute stress can make some people lose weight, chronic stress, such as long-term job insecurity, might cause some to put on pounds.
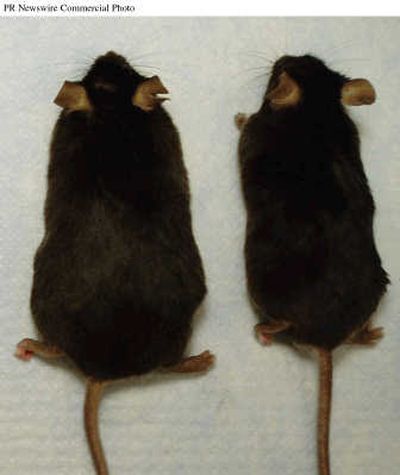
To explore this, Zukowska and her colleagues subjected mice to chronic stress – either standing in cold water an hour a day or being caged with a more aggressive alpha mouse for 10 minutes a day – and then gave them standard feed or a high-fat, high-sugar diet similar to the junk food fare many consume.
After two weeks, only the mice that were both stressed and fed the junk-food diet gained a significant amount of weight, accumulating about twice as much fat in their bellies as non-stressed mice that consumed the same diet.
“This tells me it’s not just the stress. It’s the combination of stress and the high-fat, high-sugary rich diet – that is the humongous combo,” Zukowska said.
Moreover, the stressed-out junk-food eaters put on the worst kind of fat – deposited around their abdomens and laced with hormones and other chemical signals that promote illness. After three months, the animals became obese and developed the constellation of health problems that obese humans often get – high blood pressure, early diabetes, high cholesterol – an increasingly common condition known as metabolic syndrome.
“By treating the mice the way humans are treated, which is introducing a chronic stress from which they can not escape and introducing this abundance of food, we mimicked what happens in American society,” Zukowska said.
When the researchers examined the animals’ fat tissue, they discovered sharply elevated concentrations of a substance called neuropeptide Y (NPY), a chemical messenger produced by nerves in the body, including fat. They also had far higher levels of a molecular partner NPY needs to work, known as the neuropeptide Y2R receptor.
After confirming the role of NPY in fat formation in additional studies in genetically engineered mice, the researchers showed in laboratory experiments that NPY induces the growth of immature fat cells, coaxes mature fat cells to get bigger, and promotes blood vessels necessary to sustain fat tissue.
The researchers also demonstrated that injecting a substance that blocks NPY prevented mice from accumulating fat even if they were stressed and ate a high-fat diet, and could shrink fat deposits by 40 percent to 50 percent within two weeks.
“It just melts the fat. It’s incredible,” said Zukowska.
On the flip side, when the researchers inserted pellets containing NPY under the skin of mice and three monkeys, they were able to stimulate fat growth, suggesting the approach could replace skin fillers and other cosmetic and reconstructive surgical techniques.